Lab 1.2: REST API Authentication & ‘example’ Templates¶
One of the many basic concepts related to interaction with REST API’s is how a particular consumer is authenticated to the system. BIG-IP supports two types of authentication: HTTP BASIC and Token based. It’s important to understand both of these authentication mechanisms, as consumers of the API will often make use of both types depending on the use case. This lab will demonstrate how to interact with both types of authentication.
Task 1 - Import the Postman Collection & Environment¶
In this task you will Import a Postman Collection & Environment for this lab. Perform the following steps to complete this task:
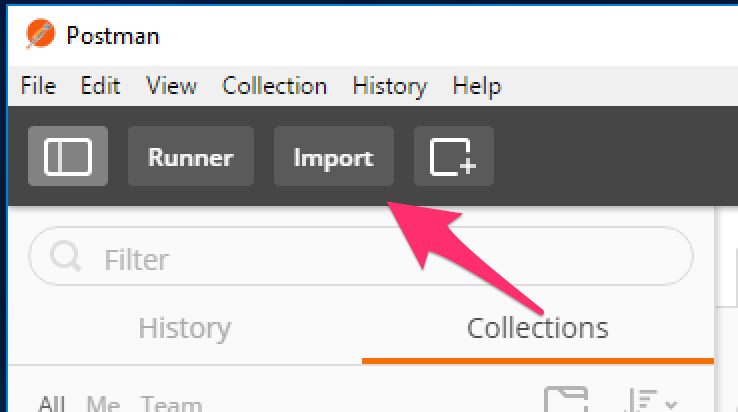
Open the Postman tool by clicking the
 icon of the desktop of
your Linux Jumphost
icon of the desktop of
your Linux JumphostClick the ‘Import’ button in the top left of the Postman window
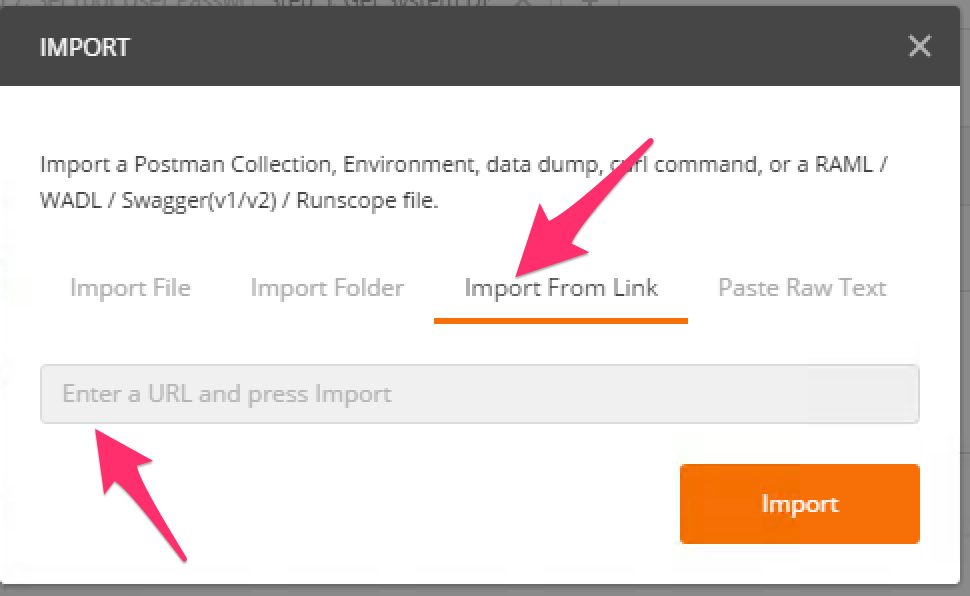
Click the ‘Import from Link’ tab. Paste the following URL into the text box and click ‘Import’
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jarrodlucia/bigip_elk_server/develop/postman_collections/F5_Automation_Orchestration_Intro.postman_collection.json
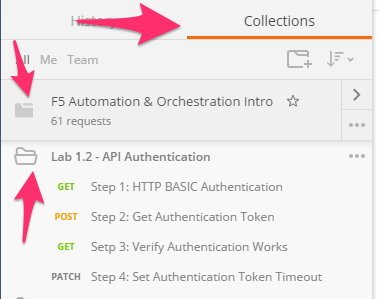
You should now see a collection named ‘F5 Automation & Orchestration Intro’ in your Postman Collections sidebar:
Import the Environment file by clicking ‘Import’ -> ‘Import from Link’ and pasting the following URL and clicking ‘Import’:
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jarrodlucia/bigip_elk_server/develop/postman_collections/INTRO_Automation_Orchestration_Lab.postman_environment.json
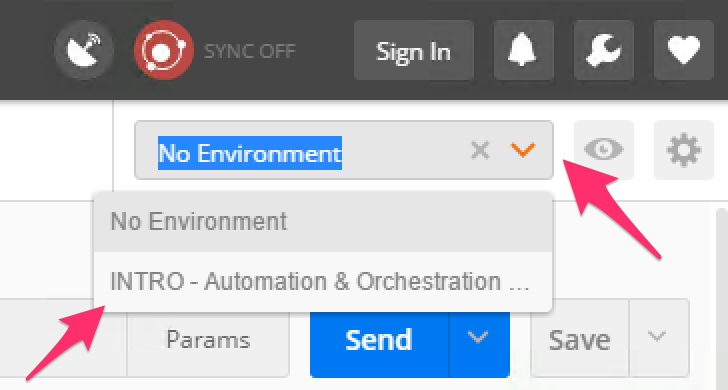
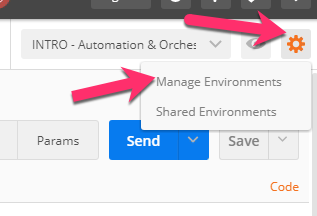
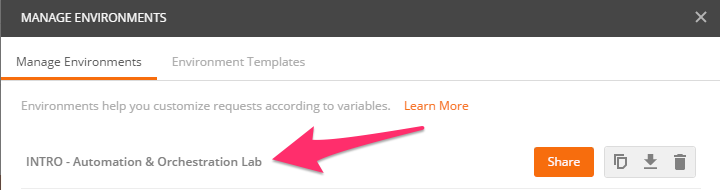
To assist in multi-step procedures we make heavy use of the ‘Environments’ capability in Postman. This capability allows us to set various global variables that are then substituted into a request before it’s sent. Set your environment to ‘INTRO - Automation & Orchestration Lab’ by using the menu at the top right of your Postman window:
Task 2 – HTTP BASIC Authentication¶
In this task we will use the Postman tool to send API requests using
HTTP BASIC authentication. As its name implies this method of
authentication encodes the user credentials via the existing BASIC
authentication method provided by the HTTP protocol. The mechanism this
method uses is to insert an HTTP header named ‘Authorization’ with a
value that is built by Base 64 encoding the string
<username>:<password>. The resulting header takes this form:
Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=
It should be noted that cracking the method of authentication is TRIVIAL; as a result API calls should always be performed using HTTPS (F5 default) rather than HTTP.
Perform the following steps to complete this task:
Click the ‘Collections’ tab on the left side of the screen, expand the ‘F5 Automation & Orchestration Intro’ collection on the left side of the screen, expand the ‘Lab 1.2 – API Authentication’ folder:
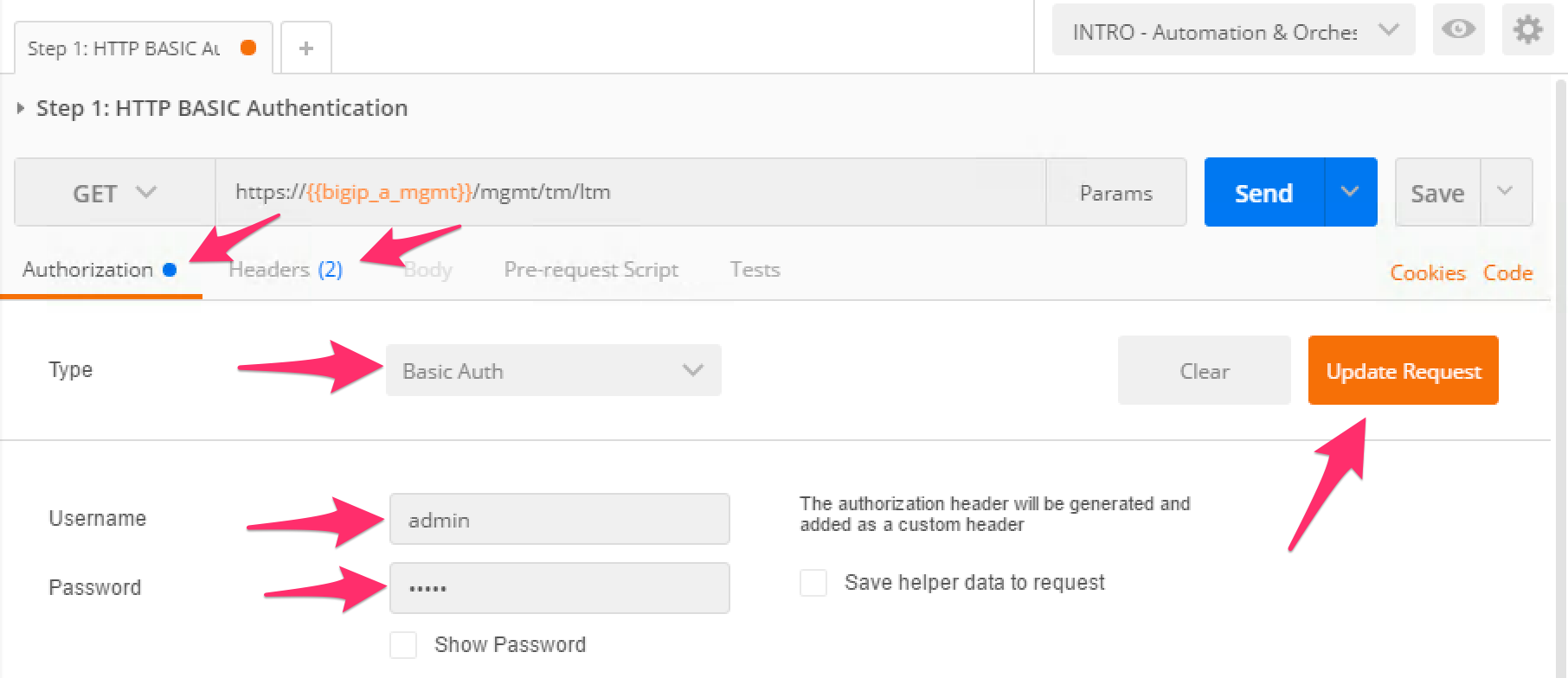
Click the ‘Step 1: HTTP BASIC Authentication’ item. Click the ‘Authorization’ tab and select ‘Basic Auth’ as the Type. Fill in the username and password (admin/admin) and click the ‘Update Request’ button. Notice that the number of Headers in the Headers tab changed from 1 to 2. This is because Postman automatically created the HTTP header and updated your request to include it. Click the ‘Headers’ tab and examine the HTTP header:
Click the ‘Send’ button to send the request. If the request succeeds you should be presented with a listing of the
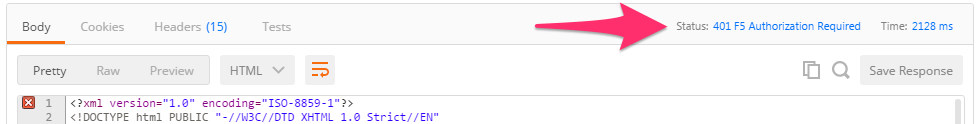
/mgmt/tm/ltmOrganizing Collection.Update the credentials and specify an INCORRECT password. Send the request again and examine the response:
Task 3 – Token Based Authentication¶
One of the disadvantages of BASIC Authentication is that credentials are sent with each and every request. This can result in a much greater attack surface being exposed unnecessarily. As a result Token Based Authentication (TBA) is preferred in many cases. This method only sends the credentials once, on the first request. The system then responds with a unique token for that session and the consumer then uses that token for all subsequent requests. Both BIG-IP and iWorkflow support token-based authentication that drops down to the underlying authentication subsystems available in TMOS. As a result the system can be configured to support external authentication providers (RADIUS, TACACS, AD, etc) and those authentication methods can flow through to the REST API. In this task we will demonstrate TBA using the local authentication database, however, authentication to external providers is fully supported.
For more information about external authentication providers see the section titled “About external authentication providers with iControl REST” in the iControl REST API User Guide available at https://devcentral.f5.com
Perform the following steps to complete this task:
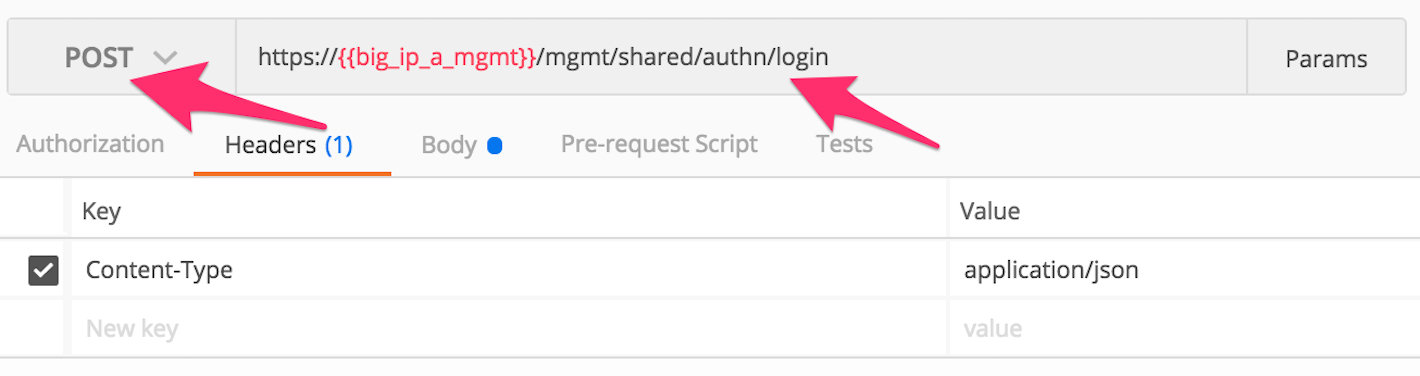
Click the ‘Step 2: Get Authentication Token’ item in the Lab 1.2 Postman Collection
Notice that we send a POST request to the
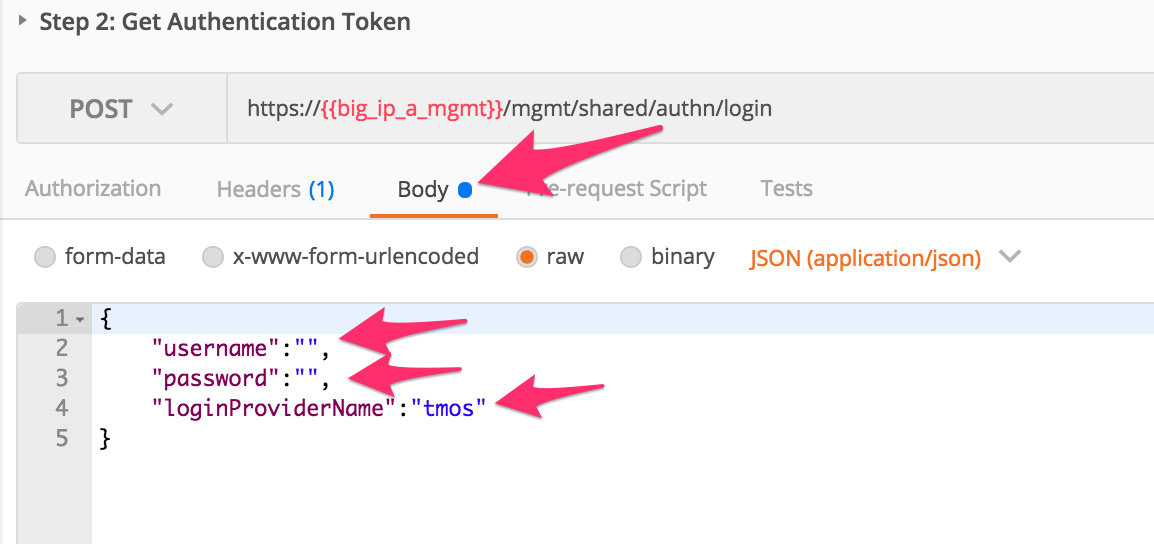
/mgmt/shared/authn/loginendpoint.Click the ‘Body’ tab and examine the JSON that we will send to BIG-IP to provide credentials and the authentication provider:
Modify the JSON body and add the required credentials (admin/admin). Then click the ‘Send’ button.
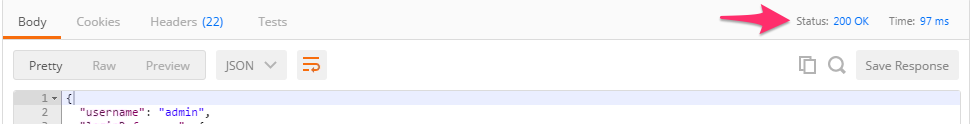
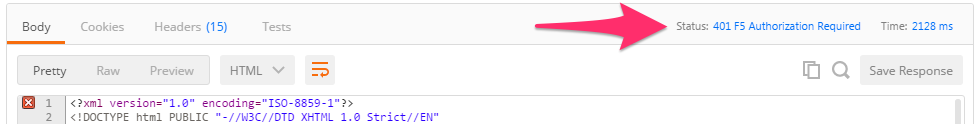
Examine the response status code. If authentication succeeded and a token was generated the response will have a 200 OK status code. If the status code is 401 then check your credentials:
Successful:
Unsuccessful:
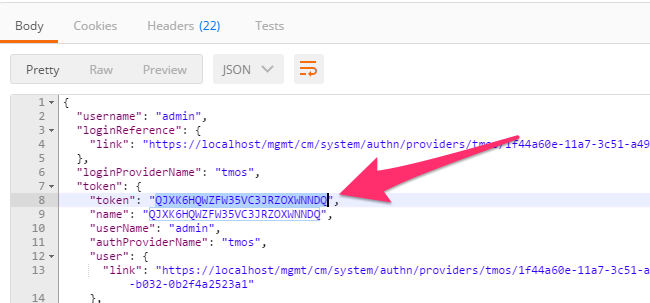
Once you receive a 200 OK status code examine the response body. The various attributes show the parameters assigned to the particular token. Find the ‘token’ attribute and copy it into your clipboard (Ctrl+c) for use in the next step:
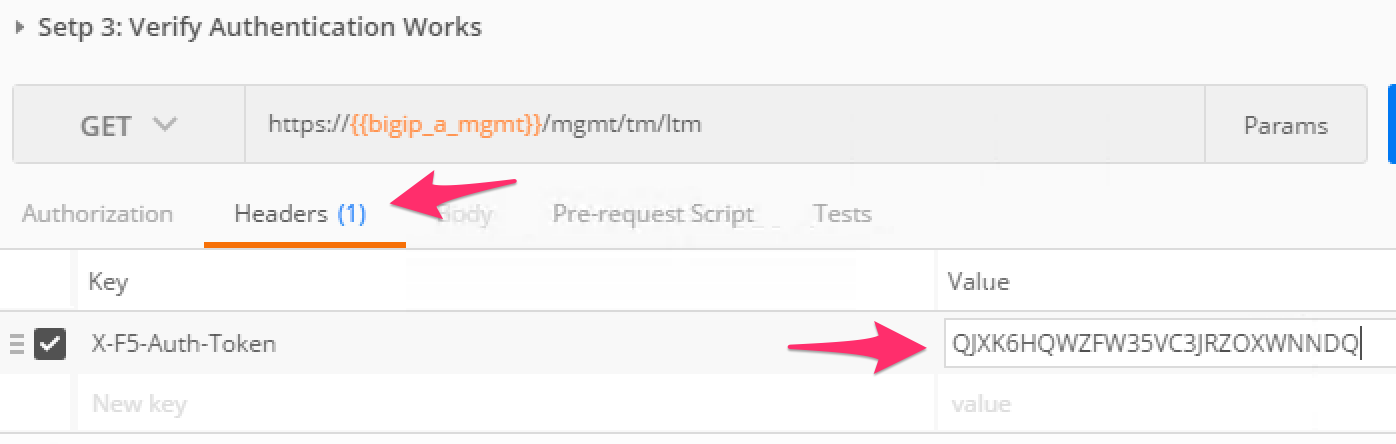
Click the ‘Step 3: Verify Authentication Works’ item in the Lab 1.2 Postman collection. Click the ‘Headers’ tab and paste the token value copied above as the VALUE for the
X-F5-Auth-Tokenheader. This header is required to be sent on all requests when using token based authentication.Click the ‘Send’ button. If your request is successful you should see a ‘200 OK’ status and a listing of the
ltmOrganizing Collection.We will now update your Postman environment to use this auth token for the remainder of the lab. Click the Environment menu in the top right of the Postman window and click ‘Manage Environments’:
Click the ‘INTRO – Automation & Orchestration Lab’ item:
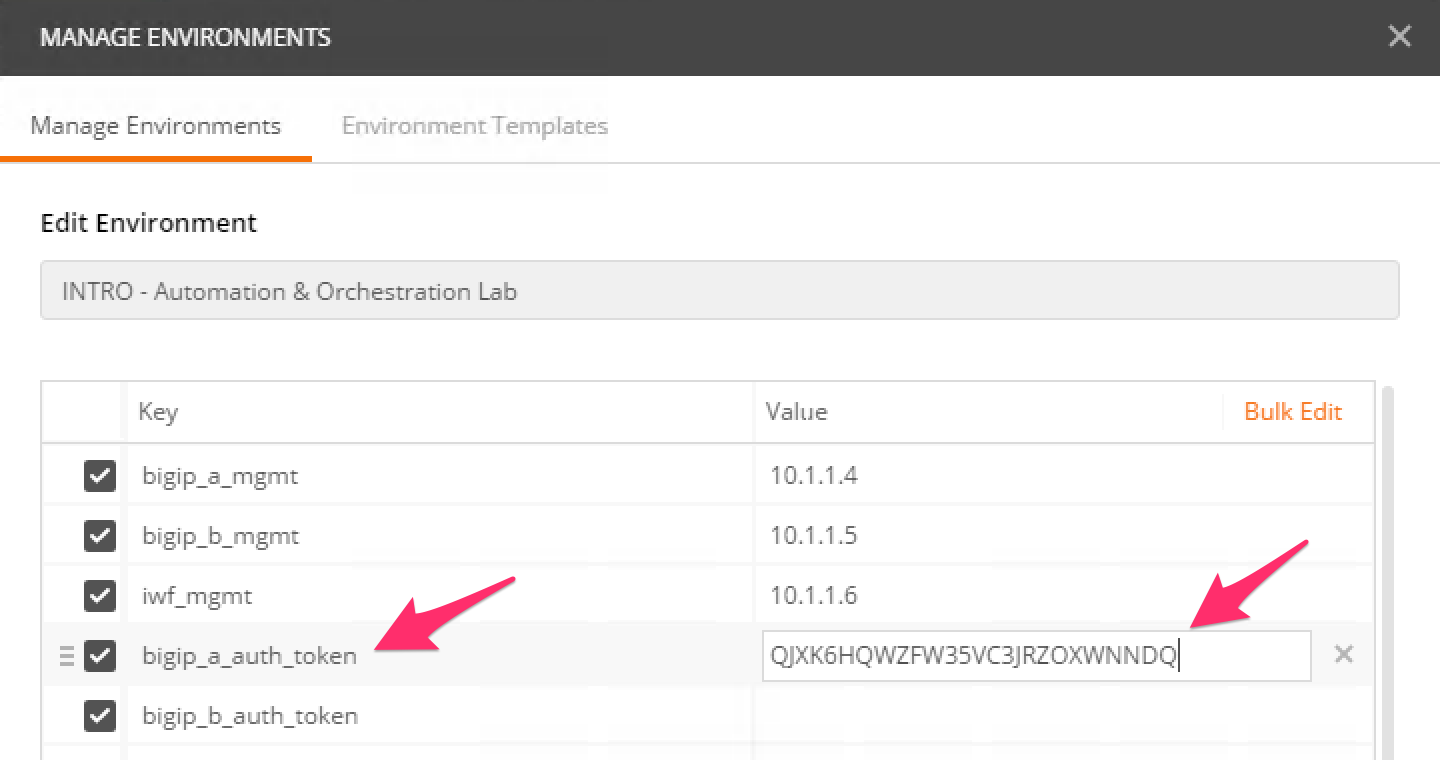
Update the value for
bigip_a_auth_tokenby Pasting (Ctrl-v) in your auth token:Click the ‘Update’ button and then close the ‘Manage Environments’ window. Your subsequent requests will now automatically include the token.
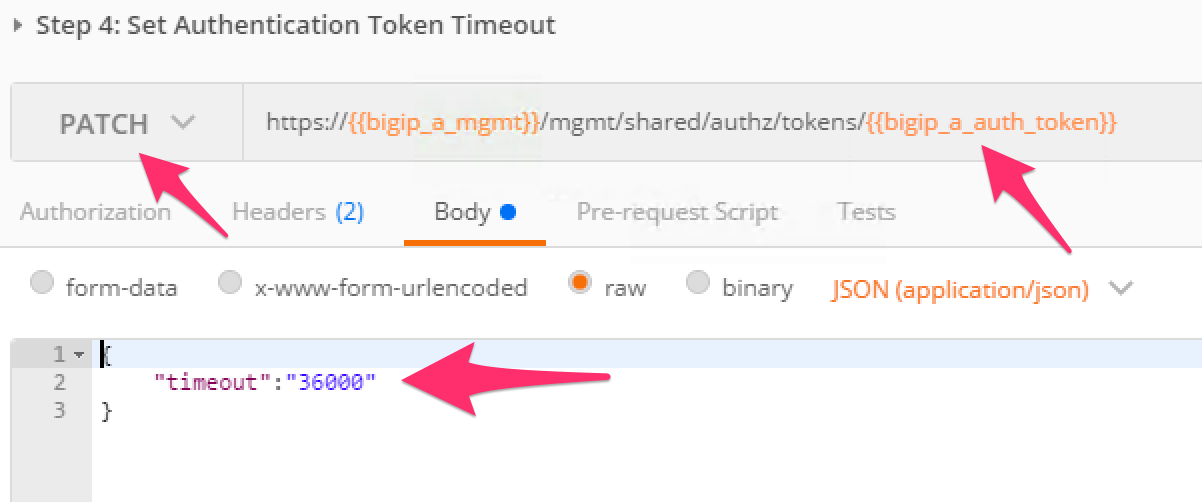
Click the ‘Step 4: Set Authentication Token Timeout’ item in the Lab 1.2 Postman collection. This request will PATCH your token Resource (check the URI) and update the timeout attribute so we can complete the lab easily. Examine the request type and JSON Body and then click the ‘Send’ button. Verify that the timeout has been changed to ‘36000’ in the response:
Task 4 – Get a pool ‘example’ Template¶
In order to assist with REST API interactions you can request a template of the various attributes of a Resource type in a Collection. This template can then be used as the body of a POST, PUT or PATCH request as needed.
Perform the following steps:
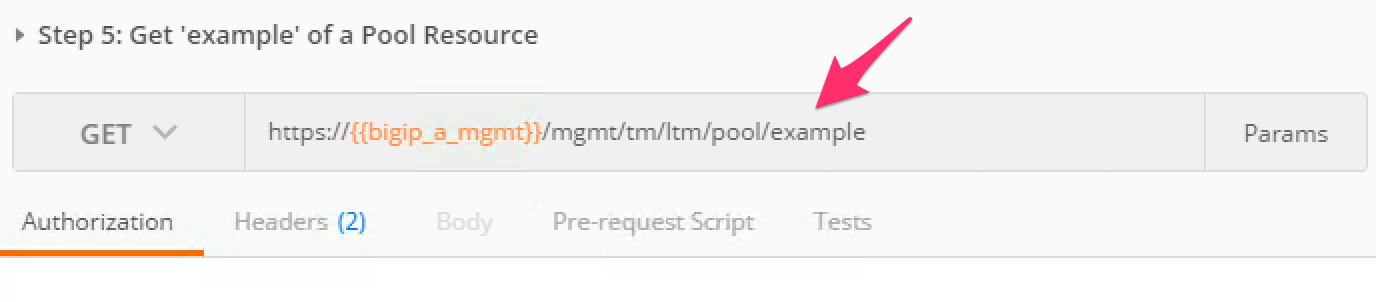
Click the ‘Step 5: Get ‘example’ of a Pool Resource’ item in the Lab 1.2 Postman collection
Examine the URI. Notice the addition of example at the end of the collection name:
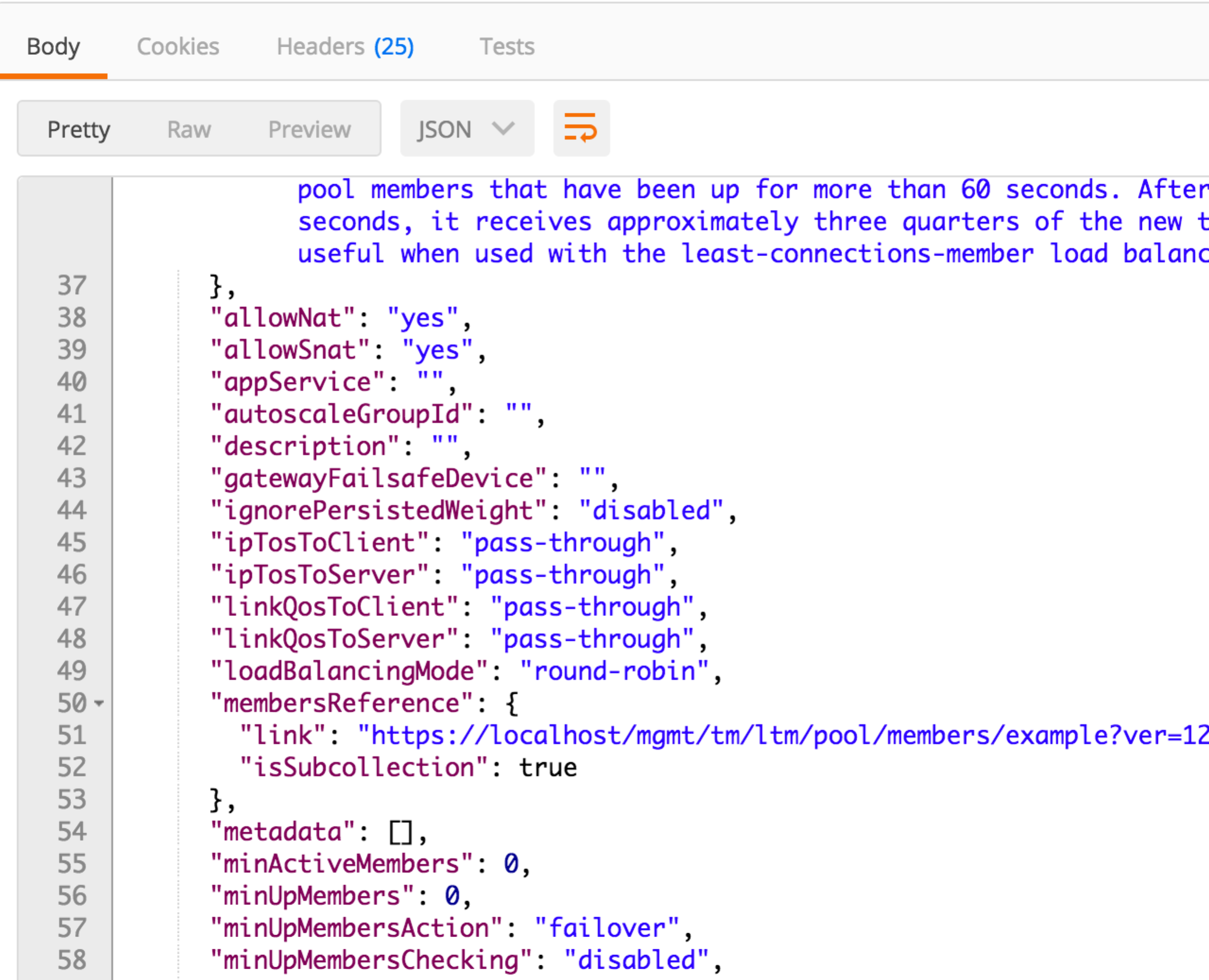
Click ‘Send’ and examine the FULL response. You will see descriptions and then all the attributes for the Pool resource type. The response also shows the default values for the attributes if applicable: